React State Management Libraries
I’m going to explore various React state management libraries, comparing their features, pros, and cons to help you choose the best solution for your application today.
Below is the data from the past 5 years, and it seems that React-Redux has been the most widely used.
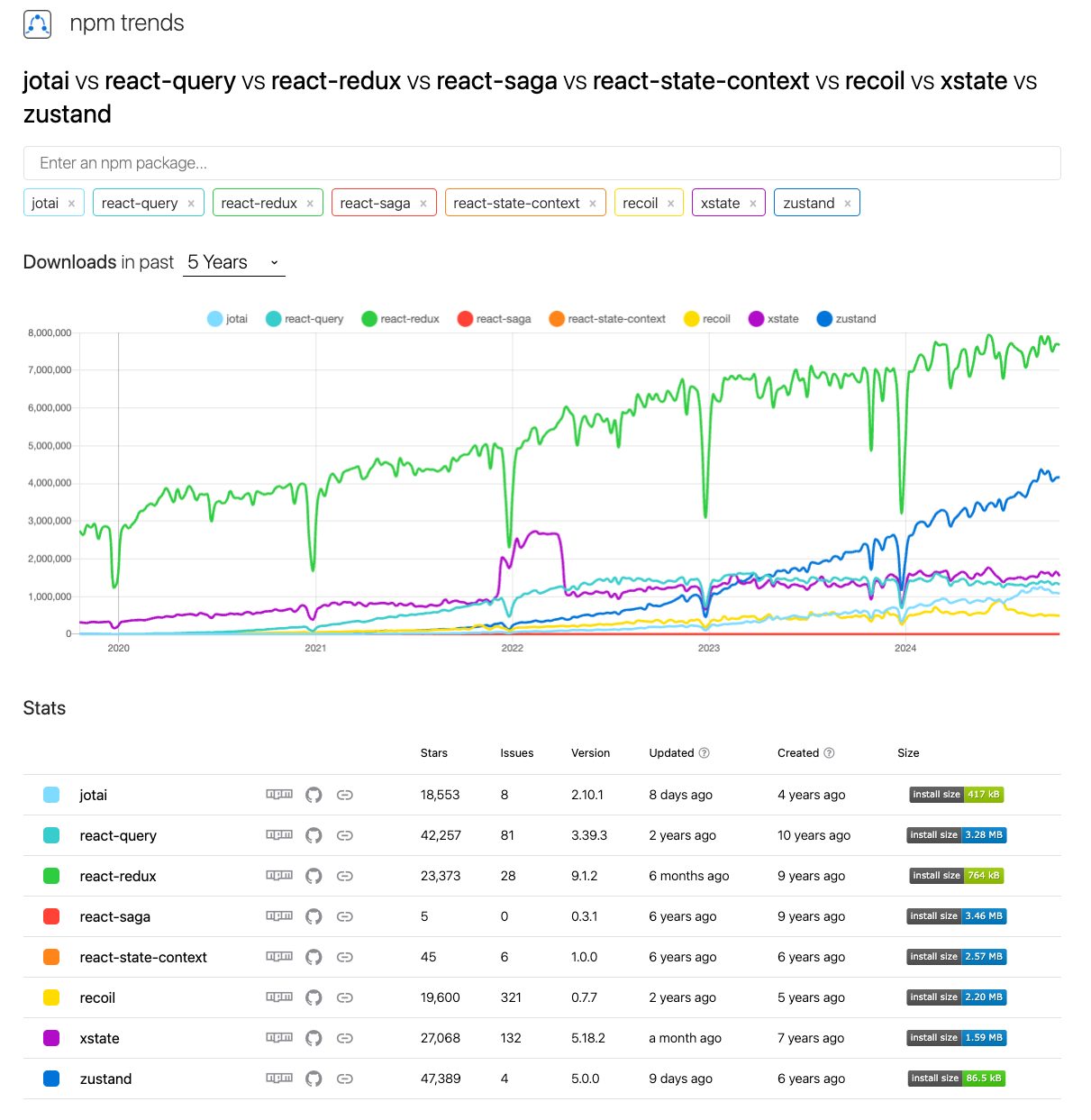
Now, let’s dive deeper into some of the most popular React state management libraries, comparing their features and use cases to help you make an informed decision.
1. React Context API
Features:
- Built-in state management tool in React.
- Suitable for managing global state in small applications.
Pros:
- Simple to use and integrates well with React.
- No need for external libraries.
Cons:
- Can lead to performance issues and code complexity in larger applications.
2. Redux
Features:
- Centralizes global state management.
- Ideal for large-scale applications with complex state management needs.
Pros:
- Improves predictability of state changes.
- Strong integration with debugging tools.
Cons:
- Initial setup can be complex.
- Requires a significant amount of boilerplate code.
3. MobX
Features:
- Supports reactive programming with observable state objects.
- Good for applications with frequently changing or asynchronous state.
Pros:
- Simplifies state management with a clean, reactive approach.
- Automatically handles state updates.
Cons:
- Less explicit state management can make it harder to track state changes.
4. Recoil
Features:
- Developed by Facebook, integrates seamlessly with React.
- Specializes in managing hierarchical states.
Pros:
- Simple, intuitive API.
- Easy asynchronous state management.
Cons:
- Newer library with a smaller ecosystem compared to others.
5. Zustand
Features:
- Lightweight state management library.
- Uses a minimalistic Flux architecture.
Pros:
- Very easy to use and lightweight.
- Ideal for small projects.
Cons:
- May not be suitable for larger applications with complex state management needs.
6. Jotai
Features:
- Uses atoms to manage state in a modular way.
- Designed for small, independent state management tasks.
Pros:
- Lightweight and easy to split state management into smaller parts.
- Minimalistic and simple to use.
Cons:
- May become complex to manage in larger applications.
7. XState
Features:
- Utilizes state machines and statecharts to define and manage state transitions.
- Suitable for applications that require well-defined state transitions.
Pros:
- Increases predictability and readability of state management.
- Excellent for complex state transition management.
Cons:
- Learning curve involved with understanding state machines.
- May be overkill for simple applications.
8. React Query
Features:
- A library focused on managing server state, including data fetching, caching, synchronization, and updating.
- Designed to simplify the management of remote data in React applications.
Pros:
- Simplifies and automates data fetching logic.
- Provides built-in caching and background synchronization.
- Reduces boilerplate for server data management.
- Automatically handles request status like loading, error, and success states.
Cons:
- Primarily focuses on server state, not suitable for managing complex client-side state.
- Requires understanding of caching and server state management concepts.
Local State and Global State Management with React Query
React Query is specifically designed for managing server state. However, local state and global state management should still be handled separately with appropriate tools:
-
Local State (Local Component State):
- Managed using React’s built-in hooks such as
useStateanduseReducer. - Best for state that is local to a single component, like form inputs or toggles.
- Managed using React’s built-in hooks such as
-
Global State (Application-wide State):
- Managed using state management libraries like React Context API, Redux, Recoil, Zustand, etc.
- Used for state that needs to be shared across multiple components, like user authentication status, themes, or global application settings.
Combining React Query with Other State Management Tools
React Query can be combined with other state management tools to provide a complete state management solution:
-
React Query + React Context API:
- Use React Query for managing server state (e.g., data fetching and caching).
- Use Context API for lightweight global state management (e.g., theme toggling, simple app-wide settings).
-
React Query + Redux:
- Use Redux to manage global client-side state that requires more complex logic or middleware (e.g., user authentication, complex UI state).
- Use React Query for server state management to handle data fetching and synchronization with remote APIs.
-
React Query + Recoil:
- Use Recoil for managing complex global state where components need to share state efficiently.
- React Query is used for managing and synchronizing server state, such as fetching data from APIs and caching.
-
React Query + Zustand:
- Zustand is ideal for managing local or lightweight global state with minimal boilerplate.
- Combine Zustand with React Query for applications that need both simple state management and advanced server state handling.
React Query effectively handles all things related to server state, while traditional state management libraries (Redux, Recoil, Zustand, etc.) are best suited for client-side state (both local and global). Choosing the right combination depends on the specific requirements of your application.

